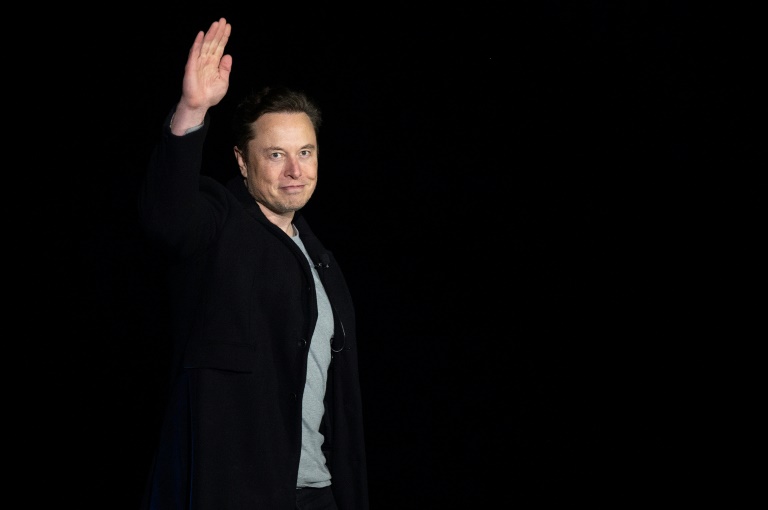
Since buying Twitter, Elon Musk has made radical changes that have sparked fears for the future of the platform, from firing half the staff to restoring ex-president Donald Trump’s account and temporarily suspending those of several journalists.
On Tuesday, he said he would step down as CEO after a Twitter poll he launched on his leadership found that most users wanted him to go.
AFP looks back at a rollercoaster two months at “the bird”.
– Enter Elon –
Musk, the world’s second-richest richest man and CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, buys Twitter in late October for $44 billion after months of on-off negotiations.
“Let the good times roll,” he tweets after the deal is sealed on October 28. He becomes the sole director of the company after dissolving its corporate board.
– ‘Content moderation council’ –
In one of his first moves, the self-declared free speech absolutist announces he will form a “content moderation council”, in a nod to concerns that Twitter could become a free-for-all platform for disinformation and hate speech.
– Monthly charge –
On November 1, Musk announces the site will charge $8 per month to verify the accounts of celebrities and companies — a service that used to be free. But the November 6 launch of the Twitter Blue subscription plan goes awry. Musk is forced to suspend the move after an embarrassing rash of fake accounts alarm advertisers.
– Brands step back –
Top global companies, including General Mills and Volkswagen, suspend their advertising on Twitter on November 3 as they monitor the new direction the company will take.
– Massive layoffs –
On November 4, half of Twitter’s 7,500-strong staff are made redundant, sending shockwaves through Silicon Valley.
Musk tweets that “unfortunately there is no choice when the company is losing over $4M/day”.
– Regulator’s ‘concern’-
The chaos draws a rare warning on November 10 from the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), the US authority that oversees consumer safety.
“We are tracking recent developments at Twitter with deep concern,” says an FTC spokesperson.
– Ultimatum to staff –
Musk delivers an ultimatum to Twitter staff on November 16, asking them to choose between being “extremely hardcore” and working long hours, or losing their jobs. He gives them a day to decide.
Large numbers of staff quit.
– Trump reinstated –
Musk reinstates the account of banned former president Donald Trump after conducting a poll of users, a narrow majority of whom support the move.
A few days later he announces an “amnesty” for all banned Twitter accounts.
– Covid controversy –
In late November, Twitter says it is no longer enforcing a policy of combatting Covid-19 disinformation. Musk had fiercely opposed Covid restrictions.
– Kanye suspended –
Musk revises his promises of unfettered free speech after rapper Kanye West tweets a picture that appears to show a swastika interlaced with a Star of David. His account is suspended for “incitement to violence”.
– Twitter Blue take two –
In mid-December Musk relaunches Twitter Blue. This time, Twitter conducts a review of the account before giving it the coveted blue check mark.
– Journalists suspended, then reinstated –
On December 15, Twitter suspends the accounts of more than a half-dozen journalists, including reporters from CNN, The New York Times, and The Washington Post.
Musk accuses them of endangering his family through their reporting on Twitter’s shutdown of an account that tracked flights of his private jet.
The EU threatens to sanction the company.
On December 17 some of the accounts are reactivated.
– Musk to step down –
On December 19, Twitter users vote by 57.5 percent to oust Musk as CEO in a poll he organised and promises to honour. A day later he says he will resign “as soon as I find someone foolish enough to take the job”.

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months ago
 Business4 months ago
Business4 months ago
 Events6 months ago
Events6 months ago
 People4 months ago
People4 months ago
 Events3 months ago
Events3 months ago